Learning to Place (L2P) is an algorithm designed to predict heavy-tail distributed outcomes. This methodology is currently under review.
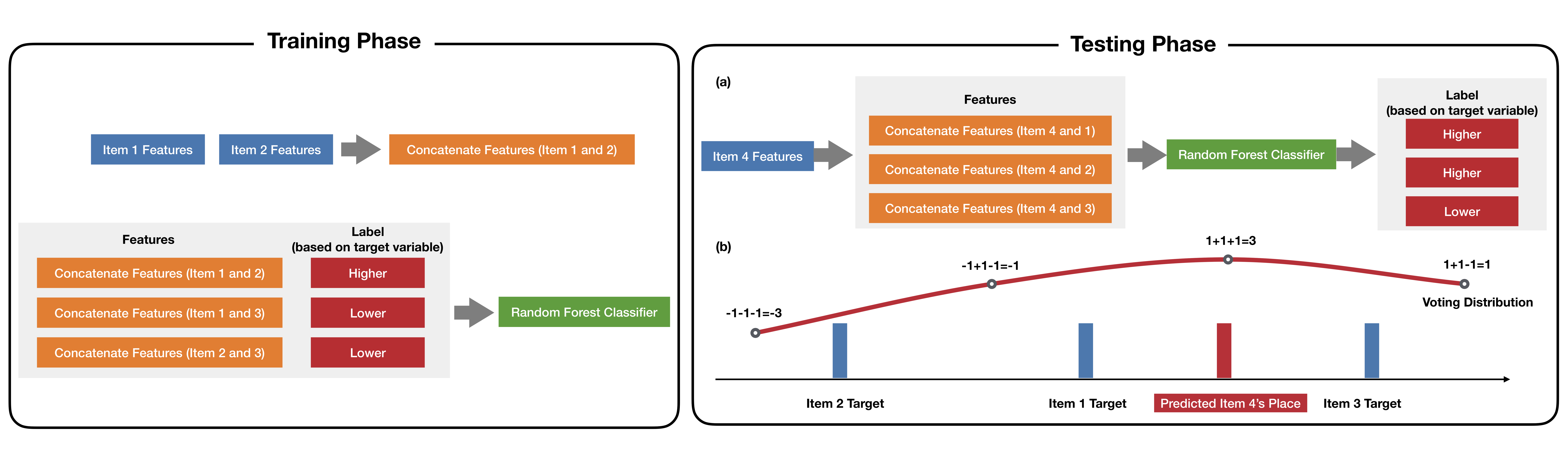
Abstract: Many real-world prediction tasks have outcome (a.k.a., target) variables that have characteristic heavy-tail distributions. Examples include copies of books sold, auction prices of art pieces, and sales of movies in the box office. Accurate predictions for the “big and rare” instances (e.g., the best-sellers, the box-office hits, etc) is a hard task. Most existing approaches heavily under-predict such instances because they cannot deal effectively with heavy-tailed distributions. We introduce Learning to Place (L2P), which exploits the pairwise relationships between instances to learn from a proportionally higher number of rare instances. L2P consists of two phases. In Phase 1, L2P learns a pairwise preference classifier: is instance A > instance B?. In Phase 2, L2P learns to place an instance from the output of Phase 1. Based on its placement, the instance is then assigned a value for its outcome variable. Our experiments, on real-world and synthetic datasets, show that our L2P approach outperforms competing approaches and provides explainable outcomes.
Algorithm
Usage
# Test code
import numpy as np
from LtP import *
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
X_train = np.array([[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
y_train = np.array([9, 56, 11, 4, 4, 6, 12])
placing = LearningToPlace(method="voting", efficient=True, clf=RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=100, n_jobs=-1, random_state=0))
placing.fit(X_train, y_train)
X_test = np.array([0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1])
predict = placing.predict(X_test)
print("Prediction: %s" % predict)
How to cite
Xindi Wang, Onur Varol, and Tina Eliassi-Rad. L2P: Algorithm for estimating heavy-tailed outcomes. (under review)